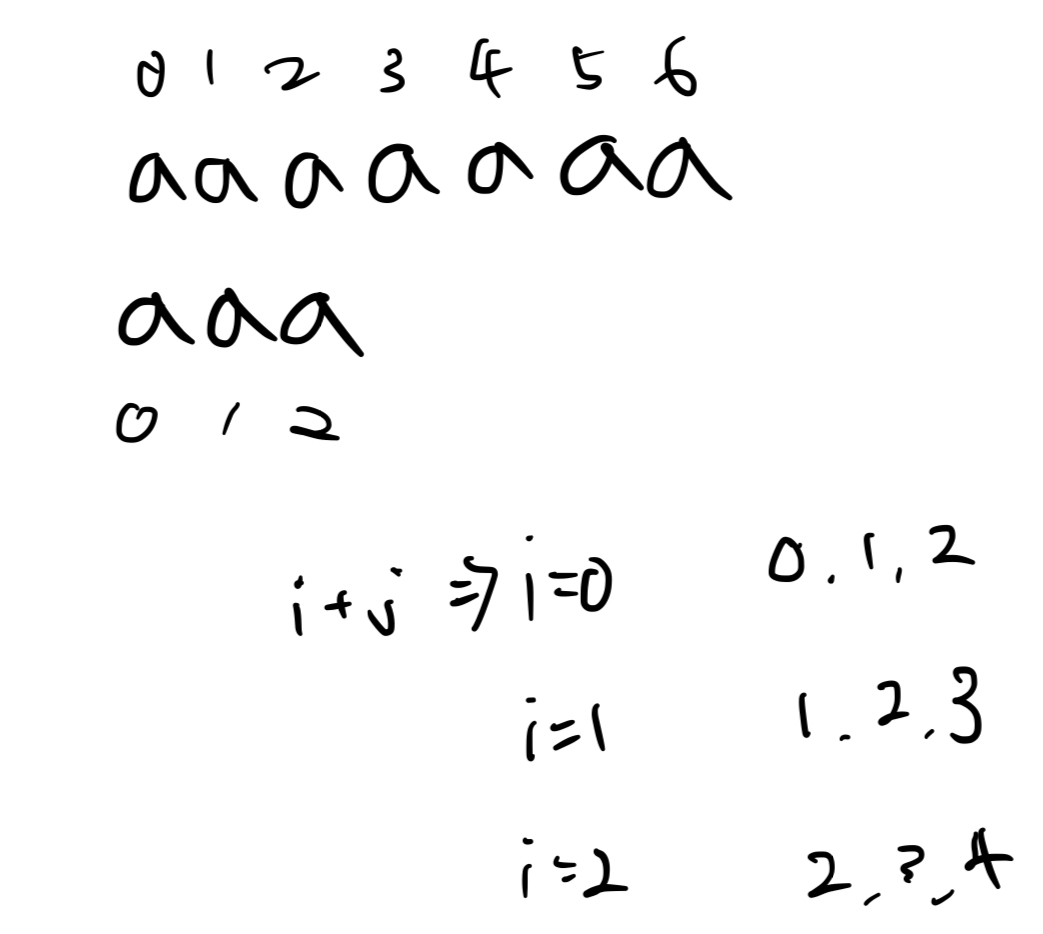Ch01 - 문자열
Last updated -
2024년 11월 21일
Edit Source
패스트캠퍼스 핵심유형 20개로 한 번에 끝내는 알고리즘 코딩테스트 with Java 강의를 정리한 내용
# 문자열
- 문자로 구성된 자료형
- String 클래스를 지원함
- String은 불변이라 인스턴스 생성되면 수정 못함
- 부분적으로 변경할 수는 없고 새로 만들어야함
charAt() : String 인덱스에 해당하는 char 출력
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| char[] arr = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
arr[2] = 'D';
System.out.println(arr);
// ABD
String str = "ABC";
str[2] = 'D';
System.out.println(str);
// 컴파일에러
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
// C
|
# String 내용 바꾸기
String 값의 변경은 불가능하지만, 새 String을 만들어서 변경할 수 있음
- 덮어쓰기
1
2
3
4
| String str = "ABCD";
str = "ABCDE";
System.out.println(str);
// ABCDE
|
- 한글자씩 떼어난 char 배열 생성해서 수정
toCharArray() : String을 char 배열로 변경
1
2
3
4
5
6
| String str = "ABCD";
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
arr[3] = 'E';
str = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str);
// ABCE
|
substring() : String 에서 부분만 뽑아내기
1
2
3
4
| String str = "ABCD";
str = str.substring(0,2) + 'E' + str.substring(3,4);
System.out.println(str);
// ABED
|
# String 내용 비교
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| String str1 = "java";
String str2 = "java";
String str3 = new String("java");
String str4 = new String("java");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str3 == str4);
// true
// false
// false
|
- 리터럴로 생성한건 String Pool(=String Costant Pool)에 한 번만 생성되고 기존 값 참조
- 인스턴스 생성한건 Heap 영역에 매번 새로 생성됨
- 따라서
==는 참조하는 대상이 같은지를 비교하는 것이다. st3.equals(str4) 처럼 equals() 를 이용해야 String의 내용이 같은지를 물어보는 �것
# String 메서드
| Method Name | Return value | Description |
|---|
| charAt(int index) | char | index에 위치한 문자 |
| length() | int | 문자열 길이 |
| equals(Object anObject) | boolean | 문자열 값의 비교 |
| compareTo(String anotherString) | int | 두 문자열을 사전순으로 비교한 결과 |
| toCharArray() | char[] | 문자열을 변환한 char 배열 |
| toLowerCase() | String | 모든 문자를 소문자로 변경한 새 문자열 |
| toUpperCase() | String | 모든 문자를 대문자로 변경한 새 문자열 |
| contains(CharSequence s) | boolean | 문자열을 포함하는지 여부 |
replace(CharSequence target,
CharSequence replacement) | String | target을 모두 replacement로 바꾼 새 문자열 |
| split(String regex) | String[] | 정규표현식에 맞게 문자열을 여러 문자열로 분할 |
| substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | String | [beginIndex, endIndex]를 갖는 새 문자열 반환 |
| indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | int | fromIndex부터 ch 문자가 나타나는 가장 첫 인덱스 |
| … | … | … |
# 2744번 문제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
char[] arr = br.readLine().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if ('A' <= arr[i] && arr[i] <= 'Z') {
arr[i] = (char)('a' + arr[i] - 'A');
} else {
arr[i] = (char)('A' + arr[i] - 'a');
}
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
}
|
- 이렇게 아스키코드 차이인 32를 굳이 안외워도 구할 수 있다.
- 소문자로 바꾸는 과정이니까 베이스 ‘a’ 에다가 (어떤 대문자 - 대문자 기준인 ‘A’) 를 더하면 되겠네
# 1919번 문제
- 단순구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String a = br.readLine();
String b = br.readLine();
int[] countA = new int[26];
int[] countB = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length(); i++) {
countA[(a.charAt(i) - 'a')]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < b.length(); i++) {
countB[(b.charAt(i) - 'a')]++;
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (countA[i] > countB[i]) {
result += countA[i] - countB[i];
}
else if (countB[i] > countA[i]) {
result += countB[i] - countA[i];
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
|
- 중복을 메서드로 빼보기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static int[] getAlphabetCount(String str) {
int[] count = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
count[(str.charAt(i) - 'a')]++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String a = br.readLine();
String b = br.readLine();
int[] countA = getAlphabetCount(a);
int[] countB = getAlphabetCount(b);
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
result += Math.abs(countA[i] - countB[i]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
|
# 1157번 문제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static int[] AlphabetCount(String str) {
int[] count = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
count[(str.charAt(i) - 'A')]++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine().toUpperCase();
int[] count = AlphabetCount(str);
int maxCount = -1;
char maxAlphabet = '?';
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (count[i] > maxCount) {
maxCount = count[i];
maxAlphabet = (char)('A' + i);
} else if (count[i] == maxCount) {
maxAlphabet = '?';
}
}
System.out.println(maxAlphabet);
}
}
|
# 1543번 문제
pseudo-coe
1번 : 문서의 첫 글자부터 순회
1
2
3
| for (int i = 0; i < docs.length(); i++) {
}
|
2번 : 문서의 지금 글자부터 주어진 단어와 한 글자씩 비교
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| for (int i = 0; i < docs.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); j++) {
if (docs.charAt(i+j) != word.charAt(j)) {
// 문서에서 i번째 인덱스부터 시작하는 단어는
// 주어진 단어와 일치하지 않는다.
}
}
}
|
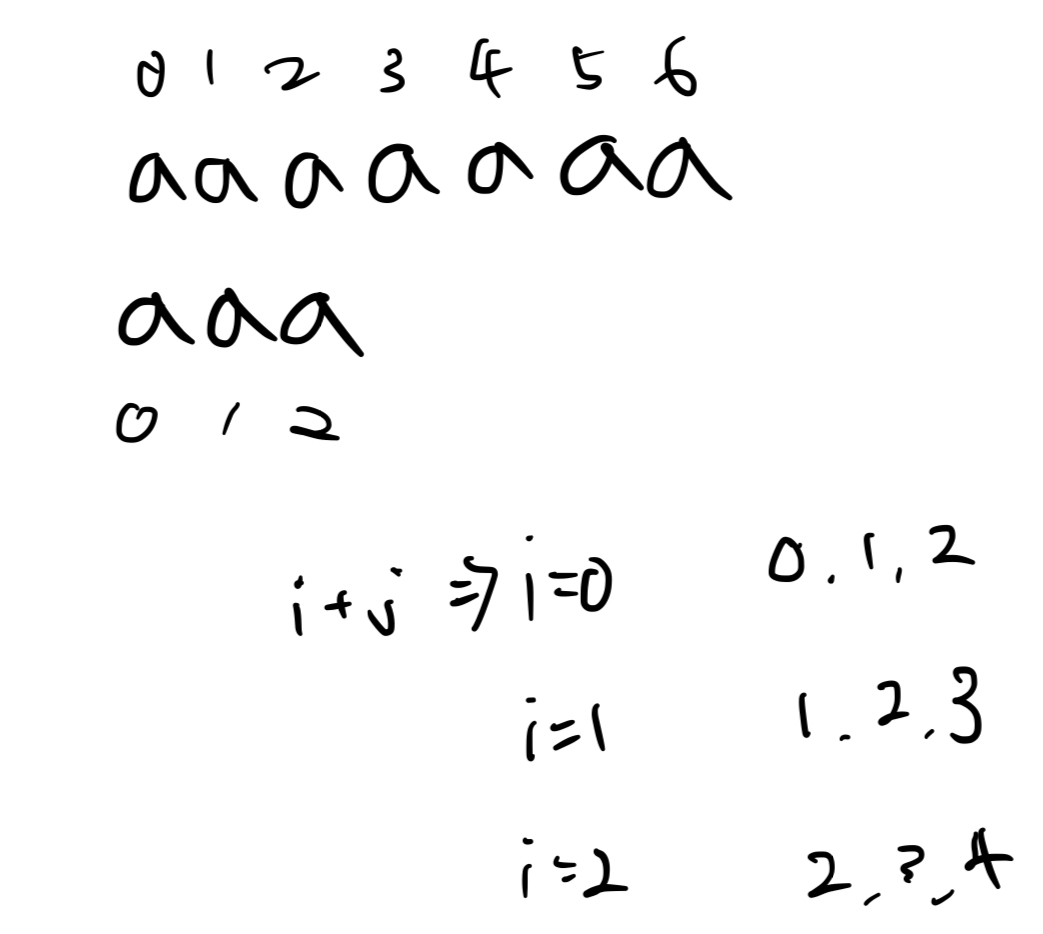
3번 : 단어와 완전히 일치하면 개수를 올리고, 해당 단어가 등장한 이후부터 2번 과정 반복
4번 : 단어와 매치되지 않았다면 다음 글자에서 2번 과정 반복
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| for (int i = 0; i < docs.length(); i++) {
boolean isMatch = true;
for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); j++) {
if (docs.charAt(i+j) != word.charAt(j)) {
isMatch = false;
break;
}
}
}
|
- 그런데, 여기서
i = docs.length() - 1이고 j = 1이면, i + j = docs.length()가 되버리니까 index 범위 넘어서 런타임에러 발생 - 인덱스를 다룰 때는 항상 범위체크하자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| for (int i = 0; i < docs.length(); i++) {
boolean isMatch = true;
for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); j++) {
if ( i + j >= docs.length() || docs.charAt(i+j) != word.charAt(j)) {
isMatch = false;
break;
}
}
if (isMatch) {
count++;
i += word.length() - 1;
}
}
|
- 중복되지 않는 단어를 찾아야함. 지금 찾은거랑 중복되면 안됨.
word.length() ? word.length() - 1 뭐 더해?- i 루프가 1을 더해주니까 그걸 감안해서 -1을 해줘야함
(( length() -1 ) + 1)
indexOf(word, startIndex) 메서드 사용하면 더 편함!
- docs 문자열의 startIndex부터 처음으로 등장하는 word 문자열을 찾음
- 찾았다면 일치하는 시작 인덱스 반환, 찾지 못하면 -1 반환
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String docs = br.readLine();
String word = br.readLine();
int count = 0;
int startIndex = 0;
while (true) {
int findIndex = docs.indexOf(word, startIndex);
if (findIndex < 0)
break;
count++;
startIndex = findIndex + word.length();
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
|
- for문에서 인덱스에 더해주던것과는 다르게 여기서는 더해주는 값이 없으니까 그냥 바로
word.length()를 해줬음
replace() 이용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String docs = br.readLine();
String word = br.readLine();
String replaced = docs.replace(word, "");
int length = (docs.length() - replaced.length()) / word.length();
System.out.println(length);
}
}
|
- docs가 “aaaaaaaa”, word가 “aaa"라고 하자.
- docs.length는 8, word.length는 3이다.
- 중복되는걸 없애고 나면 “aa"만 남게 될 것이고 length는 2이다.
- 그럼 결과적으로 몇 번 중복됐는지를 확인하려면 word의 길이만큼 나누면 되겠네
docs.length() - replaced.length()를 하고 나누기 word.length()
# 13223번 문제
HH:MM:SS 포맷에서 쪼개는 방법 3가지
- 각 단위 인덱스에서 10의 자리와 1의 자리 구해서 계산
1
2
3
4
| String time = "09:02:43"
int hour = (time.charAt(0) - '0') * 10 + (time.charAt(1) - '0');
int min = (time.charAt(3) - '0') * 10 + (time.charAt(4) - '0');
int sec = (time.charAt(6) - '0') * 10 + (time.charAt(7) - '0');
|
substring(시작인덱스, 끝인덱스) 시작 인덱스부터 끝 인덱스 전까지
1
2
3
4
| String time = "09:02:43"
int hour = Integer.parseInt(time.substring(0, 2));
int min = Integer.parseInt(time.substring(3, 5));
int sec = Integer.parseInt(time.substring(6, 8));
|
split("")
1
2
3
4
| String[] time = "09:02:43".split(":");
int hour = Integer.parseInt(time[0]);
int min = Integer.parseInt(time[1]);
int sec = Integer.parseInt(time[2]);
|
시간 계산법 2가지
- 가장 작은 단위부터 음수가 나오면 더 큰 단위에서 내림하여 가져오기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| if (sec < 0) {
sec += 60;
min--;
}
if (min < 0) {
min += 60;
hour--;
}
if (hour < 0) {
hour += 24;
}
|
- 계층적으로 표현되는 각 단위 계산 시, 가장 작은 단위로 통일
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| int now_calc = now_hour * 3600 + now_min * 60 + now_sec;
int insert_calc = insert_hour * 3600 + insert_min * 60 + insert_sec;
int result_calc = insert_calc - now_calc;
if (result_calc < 0)
result_calc += 24 * 3600;
int result_hour = result_calc / 3600;
int result_min = (result_calc % 3600) / 60;
int result_sec = result_calc % 60;
|
- 1시간 = 60분 = 3600초
- 예를 들어, 10000초라고 해보자.
10000초 = 3600 * (2시간) + 2800초2800초 = 60 * (46분) + 40초10000초 = 2시간 46분 40초
문자열 포맷 코드로 출력
| 코드 | 설명 |
|---|
| %s | 문자열(String) |
| %c | 문자 1개(character) |
| %d | 정수 (Integer) |
| %f | 부동소수 (floating-point) |
| %o | 8진수 |
| %x | 16진수 |
| %% | Literal % (문자 % 자체) |
1
| System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d", h, m, s);
|
- C에서처럼 똑같이
printf 쓰기 %02d는 정수를 출력할건데, 최소 2자리수로 맞춰주고 자리가 남으면 앞에 0으로 채우라는 의미%3.f는 소수를 출력할건데, 소수점 아래 3자리까지 출력
작은 단위로 통일한 코드 버전
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] now_time = br.readLine().split(":");
String[] insert_time = br.readLine().split(":");
int now_hour = Integer.parseInt(now_time[0]);
int now_min = Integer.parseInt(now_time[1]);
int now_sec = Integer.parseInt(now_time[2]);
int now_calc = now_hour * 3600 + now_min * 60 + now_sec;
int insert_hour = Integer.parseInt(insert_time[0]);
int insert_min = Integer.parseInt(insert_time[1]);
int insert_sec = Integer.parseInt(insert_time[2]);
int insert_calc = insert_hour * 3600 + insert_min * 60 + insert_sec;
int result_calc = insert_calc - now_calc;
if (result_calc <= 0)
result_calc += 24 * 3600;
int result_hour = result_calc / 3600;
int result_min = (result_calc % 3600) / 60;
int result_sec = result_calc % 60;
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d", result_hour, result_min, result_sec);
}
}
|
생각하고 푼 버전
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] now = br.readLine().split(":");
String[] insert = br.readLine().split(":");
int h = Integer.parseInt(insert[0]) - Integer.parseInt(now[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(insert[1]) - Integer.parseInt(now[1]);
int s = Integer.parseInt(insert[2]) - Integer.parseInt(now[2]);
if (s < 0) {
s += 60;
m--;
}
if (m < 0) {
m += 60;
h--;
}
if (h < 0) {
h += 24;
}
if (h == 0 && m == 0 && s == 0) {
h = 24;
}
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d", h, m, s);
}
}
|