Stack
Last updated -
2023년 04월 26일
Edit Source
# 스택 기본개념
스택 (Stack) : 삽입과 삭제 연산이 LIFO로 이뤄지는 자료구조
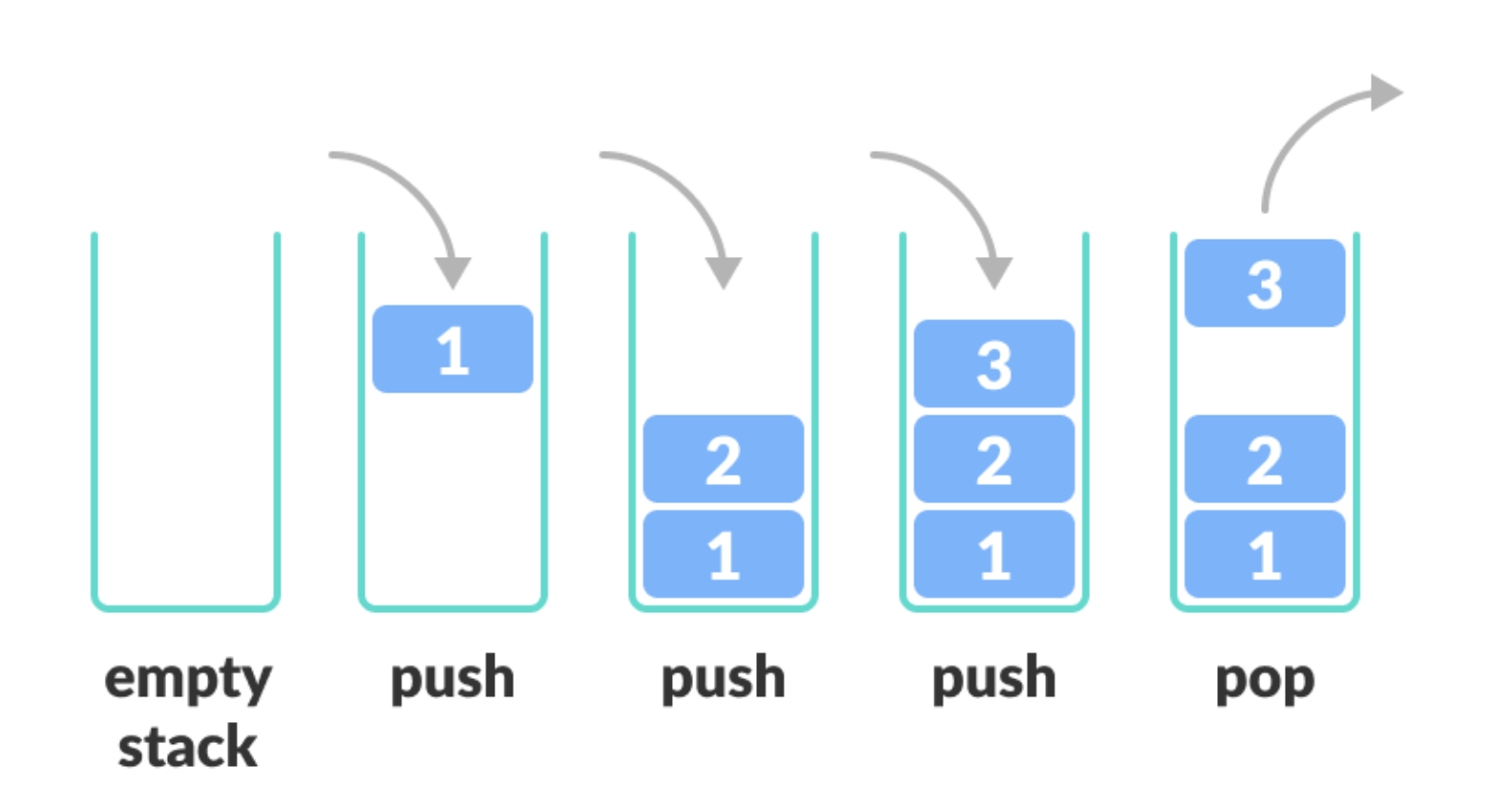
- LIFO (Last-In-First-Out, 후입선출) : 가장 나중에 들어온 것이 가장 먼저 나감
- 바로 넣었다가 거꾸로 정렬된 데이터를 꺼내고 싶을 때 유용
- 함수의 콜스택, 문자열 역순 출력, 연산자 후위표기법 등등
- DFS에서도 쓰긴 하는데.. 사실 DFS는 그냥 재귀로 하는게 …
스택을 구성하는 4가지 기능
push() : 맨 위에 데이터를 하나 쌓아올리기pop() : 맨 위에 데이터를 가져오면서 삭제peek() : 맨 위에 데이터가 뭔지 보는거isEmpty() : 스택이 비었는지 확인
# 스택 자바로 구현해보기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| import java.util.EmptyStackException;
class Stack<T> {
class Node<T> {
// 제네릭 타입인 T로 data 받음
private T data;
// 다음 노드 next
private Node<T> next;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// 스택은 맨 위의 주소만 알고 있으면 되니까
private Node<T> top;
public void push(T item) {
// push 할 아이템을 가지고 Node 를 하나 생성
Node<T> t = new Node<T>(item);
// top 앞에 생성한 Node 를 위치시킴
t.next = top;
// 이제 이 push 된 Node 가 top
top = t;
}
public T pop() {
if (top == null) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
// 맨 위에 있는 데이터를 반환하기 전에
// 그 아래에 있는 녀석을 top 으로 만들어줘야함
// 그래서 데이터 백업해놓는거
T item = top.data;
top = top.next;
return item;
}
public T peek() {
if (top == null) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return top.data;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == null;
}
}
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
}
}
// 4
// 3
// 2
// 2
// false
// 1
// true
|
# 스택 2개로 큐 1개 구현
- 스택의 특성을 이용하면
큐를 구현할 수 있다.
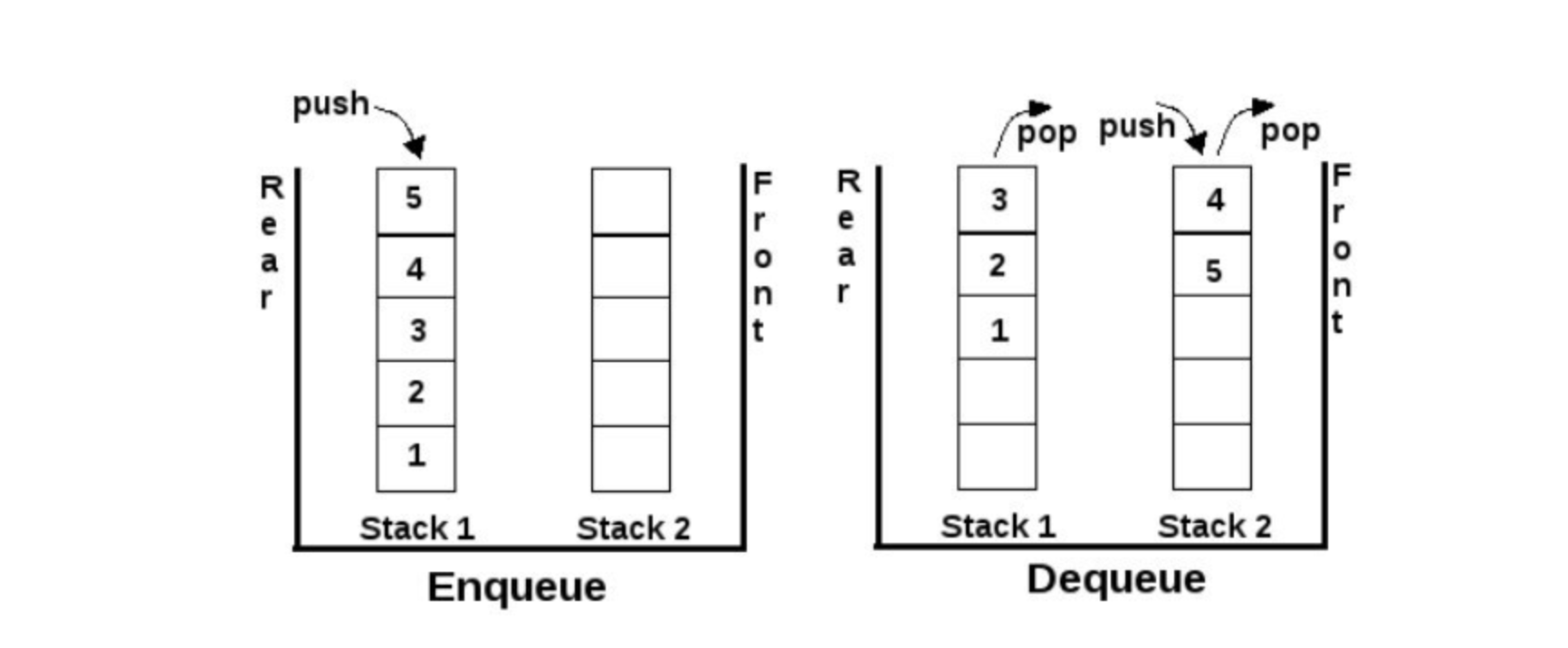
- Enqueue : 큐가
add() 할 때 새로운 데이터를 stack1에다가 push() - Dequeue : 큐가
peek(), remove() 호출 했을 때 stack2가 비어있으면- stack1에서
pop() - stack2에다가
push() - stack2에서
pop() 해서 확인
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| import java.util.Stack;
class MyQueue<T> {
Stack<T> stackNew, stackOld;
MyQueue() {
stackNew = new Stack<T>();
stackOld = new Stack<T>();
}
public int size() {
return stackNew.size() + stackOld.size();
}
public void add(T item) {
stackNew.push(item);
}
private void shiftStack() {
// stackOld 가 비어있는 상태가 아닌 경우에는
// 데이터가 mass up 될 수도 있음
if (stackOld.isEmpty()) {
while (!stackNew.isEmpty()) {
stackOld.push(stackNew.pop());
}
}
}
public T peek() {
shiftStack();
return stackOld.peek();
}
public T remove() {
shiftStack();
return stackOld.pop();
}
}
public class StackQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<Integer>();
myQueue.add(1);
myQueue.add(2);
myQueue.add(3);
System.out.println(myQueue.remove());
System.out.println(myQueue.remove());
System.out.println(myQueue.remove());
}
}
// 1
// 2
// 3
|

