선택 정렬
Last updated -
2023년 04월 26일
Edit Source
# 선택정렬 개념
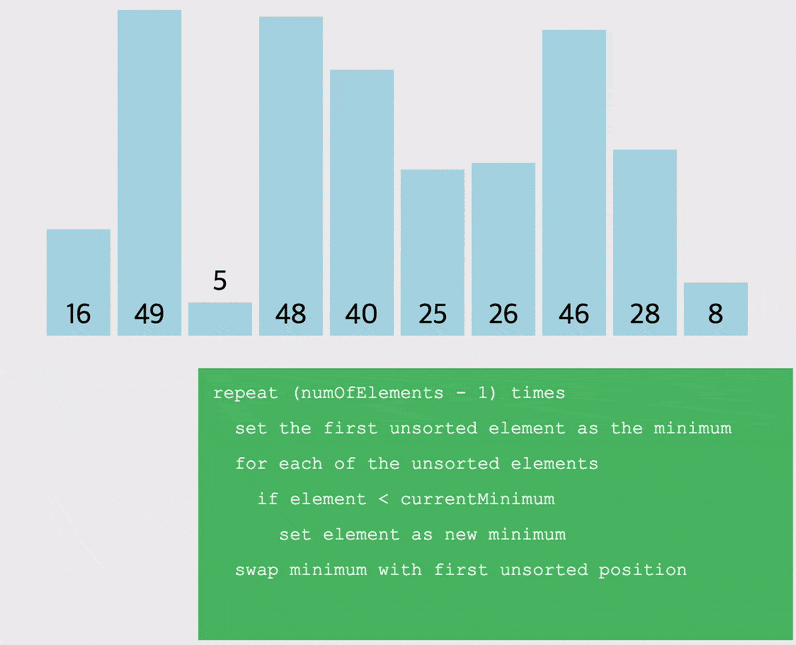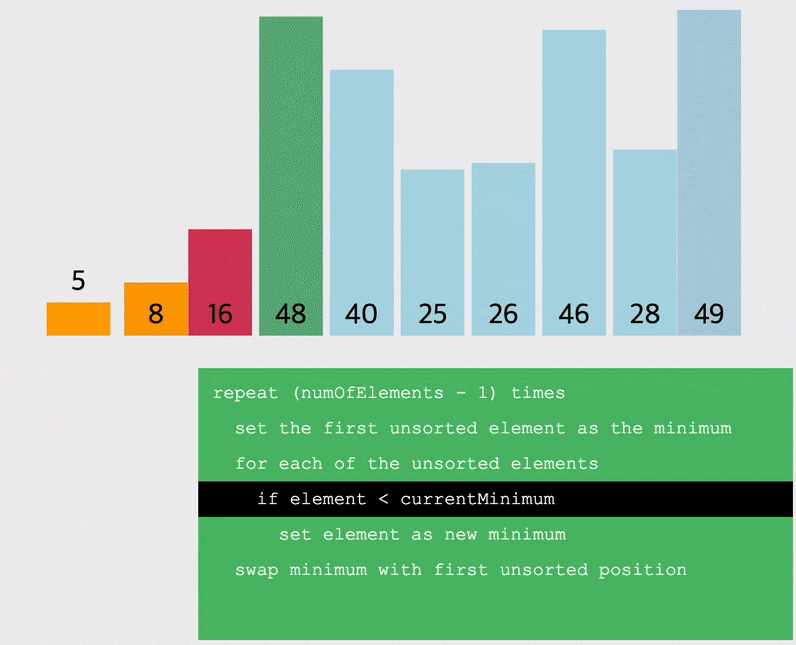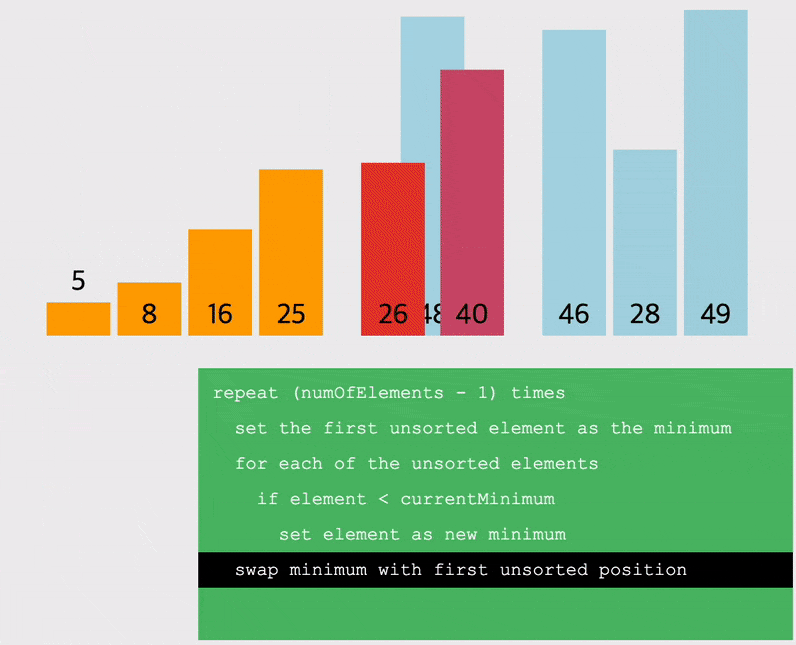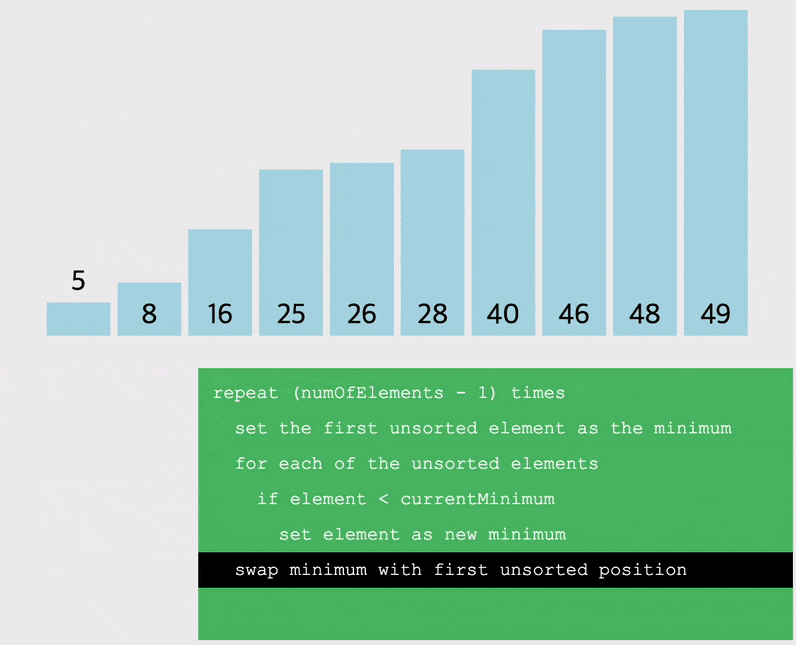
선택정렬 (Selection Sort) : 해당 순서에 원소를 넣을 위치는 이미 정해져있고, 어떤 원소를 넣을 지 선택하는 알고리즘
- 오름차순을 예시로, 배열을 돌면서 작은 값 부터 차근차근 앞으로 옮기는 정렬
- 따라서 배열을 돌면서 찾은 가장 작은 값을 저장할 변수를 선언해야함
- 해당 자리를 선택하고 그 자리에 오는 값을 찾는 과정
- 시간복잡도 : $O(n^2)$
- 최선 : $O(n^2)$, 평균 : $O(n^2)$, 최악 : $O(n^2)$
- 외부 루프를 n-1번 도는 동안, 각 자리에 와야하는 값을 구하기 위해 n-1, n-2, … , 1번 비교
- $T(n) = (n-1) + (n-2) + … + 1 = (n-1) * \frac{n}{2}$
- 공간복잡도 : $O(1)$
- 교환(swap)을 통해 정렬이 수행되므로, 추가적인 배열 공간 필요없음
- 안정성&제자리성 : 불안정 정렬(Unstable-sort), 제자리 정렬(In-place sort)
- 동일한 값을 지니는 경우, 원소들의 본래 순서가 무작위 → 불안정
- 기존 배열 이외의 추가적인 메모리를 거의 사용하지 않고 배열 안에서 교환 → 제자리
# 선택정렬 - 반복 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import java.util.Arrays;
public class Selection {
private static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
// 원소를 넣은 위치를 i로 선택
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int min_index = i;
// i + 1부터 선택한 위치 i의 값과 비교
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
// min으로 큰 것보다 정하면 j로 초기화
if (arr[j] < arr[min_index]) {
min_index = j;
}
}
// 배열, 원소 넣을 위치, 값 제일 작은 위치
swap(arr, i, min_index);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int preIndex, int postIndex) {
int temp = arr[preIndex];
arr[preIndex] = arr[postIndex];
arr[postIndex] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 2, 1, 8, 4, 5, 7};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
selectionSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
# 선택정렬 - 재귀 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| import java.util.Arrays;
public class Selection {
private static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
// 배열의 주소, 배열에서 정렬이 되지 않은 부분의 시작 위치
// 처음에는 모든 배열의 방이 정렬 안된 상태니까 첫번째 인덱스 줬음
selectionSort(arr, 0);
}
private static void selectionSort(int[] arr, int start) {
// 시작점이 배열의 마지막 인덱스보다 작을 때 재귀호출
if (start < arr.length - 1) {
// 가장 작은 방의 인덱스를 저장할 변수
// 시작 인덱스로 초기화
int min_index = start;
// 시작점부터 배열의 마지막 방까지 루프
for (int i = start; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 배열의 인덱스를 돌면서 찾은 가장 작은 값의 인덱스를 저장
if (arr[i] < arr[min_index]) min_index = i;
}
// 가장 작은 값의 인덱스를 맨 앞의 것과 swap
swap(arr, start, min_index);
selectionSort(arr, start + 1);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int preIndex, int postIndex) {
int temp = arr[preIndex];
arr[preIndex] = arr[postIndex];
arr[postIndex] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 2, 1, 8, 4, 5, 7};
System.out.println("Before Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
selectionSort(arr);
System.out.println("After Sorting: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
